Ecosystem
Ecosystem model
Development and Implementation: HCMR
Chief Scientist: Dr. George Triantafyllou
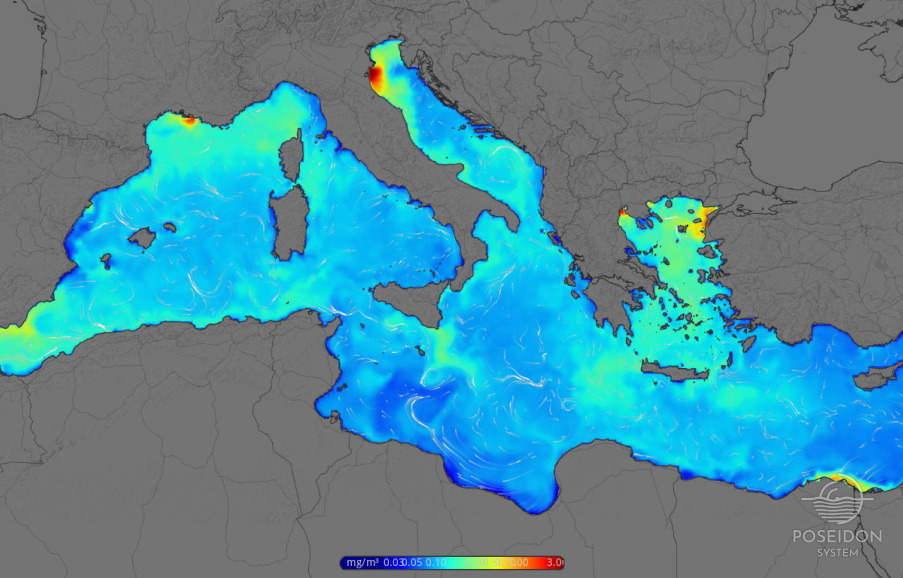
The POSEIDON ecosystem simulation tool comprises two on-line coupled models: A hydrodynamic, based on the Princeton Ocean Model (POM) (Blumberg and Mellor, 1978) with a 1/10° resolution and 24 sigma layers, and a low-trophic biogeochemical model based on the European Regional Seas Ecosystem Model (ERSEM, Baretta et al., 1995; Blackford et al., 2004; Petihakis et al. 2002). A weekly data assimilation scheme is employed on physical parameters (Korres et al., 2008) while a second order conservative upstream advection scheme (Lin et al., 1994) is used for the biological tracers.
Following the prominent characteristics of the Mediterranean Sea ecosystem, three major functional groups are included (primary producers, heterotrophs and decomposers), providing all the necessary information for the description and analysis of carbon cycling processes, with each group further subdivided into a number of subgroups following size and/or feeding method differentiations creating a web of ten state variables. Four of those belong to phytoplankton (diatoms, nanoplankton, picoplankton, dinoflagellates), three to heterotrophs (heterotrophic flagellates, microzooplankton, mesozooplankton), one to decomposers (bacteria) and two represent non-living organic matter (particulate and dissolved). Carbon flow in the web is governed by processes operating both at physiological and community level such as growth, respiration, lysis, excretion, mortality and grazing, while nutrients are loosely coupled to carbon through a variable C:N:P:Si ratio scheme.
The simulation tool is setup with initial nutrient fields extracted from the Medatlas 2002 climatology data base (http://www.ifremer.fr/medar/) and bilinearly interpolated into the model grid. To account for the effect of influx waters, all major riverine systems in the Mediterranean (Po, Rhone, Ebro, Nile) and N. Aegean (Axios, Strymon, Nestos, Evros, Pinios) are incorporated. Perpetual year inputs based on data provided by EU-SESAME project (dissolved inorganic nutrients) along with available data from the literature (Moutin et al., 1998 for Rhone; Degobbis et al., 1990 for Po; Skoulikidis et al., 1993 for N. Aegean rivers) are used. Additionally, Black sea water inputs at the Dardanelles straits are assigned through seasonally mean concentrations of dissolved inorganic nutrients (Tugrul el a., 2002) and annual mean values for dissolved organic matter, and ammonium (Polat et al. 1996).
References
Baretta, J.W., W. Ebenhoh and P. Ruardij. The European regional seas ecosystem model, a complex marine ecosystem model, Netherlands Journal of Sea Research, 33, (1995), 233-246.
Blackford, J.C., J,I,Allen, F.J. Gilbert, (2004). Ecosystem dynamics at six contrasting sites: a generic modelling study. Journal of Marine Systems, 52, 191-215.
Blumberg, A.F. and Mellor, G.L., 1978. A Coastal Ocean Numerical Model. In: J. Sunderman and K. Holtz (Editor), Mathematical Modelling of Estuarine Physics. Proceedings of the International Symposium. Springer-Verlag Berlin, Hamburg, pp. 203-214.
Degobbis, D., and M. Gilmartin. 1990. Nitrogen, phosphorus, and biogenic silicon budgets for the northern Adriatic Sea. Oceanologica Acta 13: 31-45.
Korres, G., K. Nittis, I. Hoteit and G. Triantafyllou, 2008. A high resolution data assimilation system for the Aegean Sea hydrodynamics. J. Mar. Syst. (in press).
Lin, S.J., W.C. Chao, Y.C. Sud, and G.K. Walker, 1994. A Class of the van Leer type transport schemes and its application to the moisture transport in a general circulation model, Mon. Wea. Rev., 122, 1575-1593.
Moutin T., P. Raimbault, H. L. Golterman and G. Coste, 1998. The input of nutrients by the Rhone into the Mediterranean Sea: recent observations and comparison with earlier data, Hydrobiologia 373/374, 237-246.
Petihakis, G., G. Triantafyllou, I.J. Allen, I. Hoteit, C. Dounas, Modelling the spatial and temporal variability of the Cretan Sea ecosystem, Journal of Marine Systems 36 (3-4) (2002) pp. 173-196.
Polat C. and S. Tugrul, (1996). Chemical exchange between the Mediterranean and Black Sea via the Turkish straits. CIESM Science Series No.2, Bull. De l'Institut Oceanog., 17, 167-186.
Skoulikidis, N.T., (1993). Significance evaluation of factors controlling river water composition, Env. Geo., 22, 178-185.
Tugrul, S., S.T. Besiktepe and I. Salihoglou, (2002). Nutrient exchange fluxes between the Aegean and Black Seas through the Marmara Sea, Med. Mar. Sci., 3/1, 33-42.