Meteo
The POSEIDON weather forecasting system
Development and implementation: HCMR, Department of Geography - Harokopio University of Athens - Atmospheric Modeling and Weather Forecasting Group of the University of Athens
Chief Scientist: Dr. A. Papadopoulos (2000-2018)
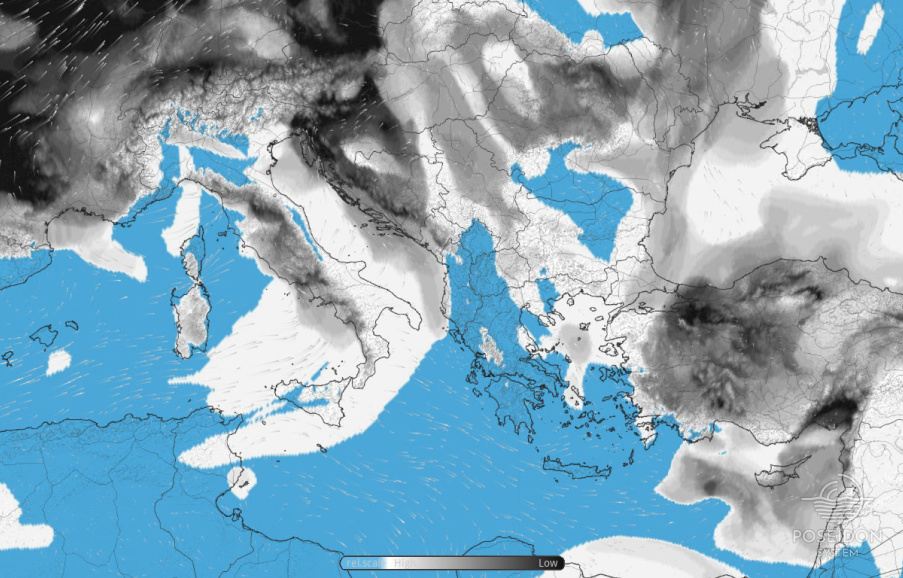
The POSEIDON weather forecasting system was initially developed in 1997-2000 in the framework of the POSEIDON-I project. The basic concept was to design a reliable and computationally efficient system that produces high accuracy weather forecasts, particularly useful for predicting local atmospheric conditions and forcing the wave, the ocean hydrodynamic and the ecosystem models of the POSEIDON system with surface fluxes of momentum, moisture, heat, radiation (short wave and long wave) and precipitation rates. The system with its nesting capability (Papadopoulos et al., 2002) became operational in October 1999 provided 72-hour forecasts in two different model domains and resolutions (1/10°x1/10° - (10 km) and 1/4°x1/4° - (25 km) grid increment). The coarser model domain covered an extended area including most of Europe, Mediterranean Sea and N. Africa, while with the finer grid increment the model was integrated over the Eastern Mediterranean. Its central component was the SKIRON/Eta model (Kallos et al., 1997), which was a modified version of the Eta/NCEP model and is coupled with a dust cycle prediction model (Nickovic at al., 2001).
A major upgrade of the system was carried out during the POSEIDON-II project (2005-2008) in collaboration with the Atmospheric Modeling and Weather Forecasting Group of the University of Athens and included: (a) the implementation of the non-hydrostatic version of the SKIRON/Eta model (Janjic et al., 2001), (b) the introduction of state-of-the-art parameterisations of all the major phases of the atmospheric dust life such as production, diffusion, advection and removal related to particle size distribution (Kallos et al., 2006), (c) a 3D data assimilation package, the Local Analysis Prediction System (LAPS) to produce high resolution analysis fields. LAPS uses the GFS/NCEP global analysis to generate 3D first guess fields, then integrates all available real-time surface and upper air observations and finally produces a high resolution analysis for the definition of the initial conditions of the atmospheric model. For the boundary conditions the GFS/NCEP global forecasts are used. The upgraded POSEIDON weather forecasting system (Papadopoulos et al., 2008) turned into operation in December 2007 and is applied on a horizontal resolution of 1/20°x1/20° (~5 km) over the domain covering the whole Mediterranean and Black Sea regions and the surrounding countries. In the vertical, 50 levels are available up to 25 mb (~25 km), while the simulation period has been enlarged to 120 hours (5 days).
In the framework of HIMIOFoTS project, a major upgrade of the LAPS 3D data assimilation package was implemented by the Geography Department of the Harokopio University of Athens in 2019, enhancing the high resolution analysis fields. LAPS domain covers entire Europe and it is currently running with GFS forecasts as background fields assimilating METAR, SYNOP and RAOB measurements in real-time. Moreover, the POSEIDON weather forecasting system was ported to a new High Performance Computer System (HPC) to ensure faster execution and better stability.
References
Janjic, Z.I., Gerrity J.P.Jr., & Nickovic, S., 2001. An Alternative Approach to Nonhydrostatic Modeling. Monthly Weather Review, 129: 1164-1178.
Kallos, G., S. Nickovic, A. Papadopoulos, D. Jovic, O. Kakaliagou, N. Misirlis, L. Boukas, N. Mimikou, G. Sakellaridis, J. Papageorgiou, E. Anadranistakis, and M. Manousakis, 1997, The regional weather forecasting system SKIRON: An overview, Proceedings of the International Symposium on Regional Weather Prediction on Parallel Computer Environments, 15-17 October 1997, Athens, Greece, 109-122.
Kallos, G., A. Papadopoulos, S. Nickovic, and P. Katsafados, 2006: “Trans-Atlantic North African dust transport: Model simulation”. Journal of Geophysical Research, 111, D09204, doi:10.1029/2005JD006207.
Nickovic, S., Kallos, G., Papadopoulos A. & Kakaliagou, O., 2001: A model for prediction of desert dust cycle in the atmosphere. Journal of Geophysical Research, 106: 18113-18129.
Papadopoulos, A., P. Katsafados, G. Kallos, and S. Nickovic, 2002. The weather forecasting system for POSEIDON-An overview. Global Atmosphere and Ocean System, 8 (2-3): 219-237.
Papadopoulos, A., P. Katsafados, E. Mavromatidis, and G. Kallos, 2008. Assessing the skill of the POSEIDON-II weather forecasting system. Abstracts books of the EuroGOOS 2008 conference.