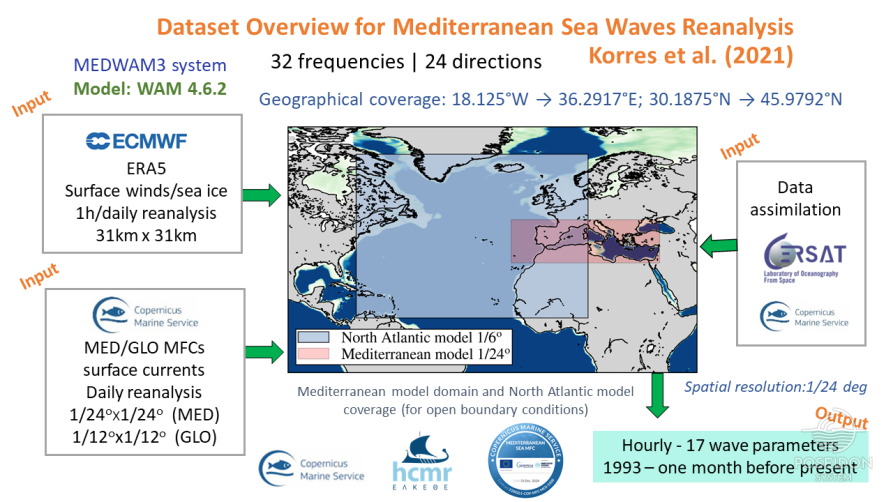
Reanalyses: A "time machine" for our oceans
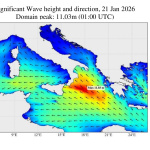
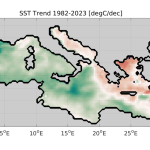
Think of reanalyses as a “time machine” for our oceans! Using mathematical models, scientists can recreate and understand ocean conditions across time, and with extensive spatial coverage – something that in-situ (local measurements) and satellite observations alone cannot achieve. Through reanalyses, oceanographers study both prevailing conditions and trends in the oceans through parameters such as wave height and sea surface temperature, thus enhancing our understanding and prediction of climate change.
The Poseidon team’s participation at the 6th International Conference for Reanalysis (ICR6), Tokyo, Japan
At ICR6, the 6th International Conference for Reanalysis held in Tokyo, representatives from leading operational centers, including ECMWF, the Japan Meteorological Agency, and the Copernicus Marine Service, gathered to discuss the latest developments and challenges in the field of reanalyses. The conference focused on improving data accuracy and expanding the applications of reanalyses, especially for scientific and societal activities. Accurate data validation is considered essential for improving predictive models and reducing uncertainties, both under normal conditions and during extreme events. Data reliability and proper validation practices are also crucial for the safe and efficient use of wave energy conversion devices.
Representing the Poseidon research group, Charikleia Oikonomou presented a new study on reanalysis data validation for wave energy applications, with the title:
“Formulating validation guidelines for marine renewable energy applications using the Copernicus Marine Mediterranean Sea waves reanalysis”
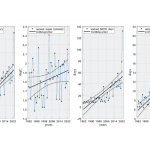
In her presentation, she highlighted validation methods using in-situ observations, using the Copernicus Marine Mediterranean Sea Waves Reanalysis, which complies with International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) standards. This database is a valuable tool for marine renewable energy studies in the Mediterranean, offering high accuracy and reliability.
Notably, approximately 75-80% of scientific studies on wave energy potential in the Mediterranean rely primarily on reanalysis data rather than satellite or in-situ data. Reanalyses provide long-term coverage with high spatial and temporal resolution across the entire Mediterranean basin, making them ideal for studying marine renewable energy sources.
This study is one of the first to apply bias correction methods on wave reanalysis data for such applications and offer guidelines for using reanalyses in the field of marine renewable energy. These methods improve the sustainability and efficiency of wave energy exploitation devices. C. Oikonomou also served as rapporteur, contributing to the overall assessment of the conference conclusions.
Poseidon’s active involvement in the Copernicus Marine Service
The Poseidon research team actively participates in the Copernicus Marine Service, producing reanalysis data and wave forecasts for the Mediterranean. Additionally, the team presented a scientific poster in collaboration with members of the Mediterranean Forecasting and Monitoring Center (MED-MFC), presented by Ali Aydogdu (CMCC) highlighting the importance of reanalyses in understanding the Mediterranean climate and analyzing extreme events.
Related references
Aydogdu, A., Miraglio, P., Pistoia, J., Moulin, A., Grandi, A., Drudi, M., Clementi, E., Korres, G., Oikonomou, C., Denaxa, D., Cossarini, G., Salon, S., and Teruzzi, A., 2024: Copernicus Marine Service Mediterranean Sea reanalysis systems, 6th WCRP International Conference on Reanalysis, Tokyo, Japan, 28 Oct – 1 Nov 2024, PR2-10.
IEC TS 62600-101 (2015) Technical specifications: Marine energy – Wave, tidal and other water current converters – Part 101: Wave energy resource assessment and characterization
Korres, G., Ravdas, M., Denaxa, D., & Sotiropoulou, M. (2021). Mediterranean Sea Waves Reanalysis INTERIM (CMEMS Med-Waves, MedWAM3I system) (Version 1) [Data set]. Copernicus Monitoring Environment Marine Service (CMEMS). https://doi.org/10.25423/CMCC/MEDSEA_MULTIYEAR_WAV_006_012_MEDWAM3I
Oikonomou, C.L.G., Denaxa, D. and Korres, G., 2024. Unlocking the Mediterranean potential: Wave energy flux and swell contributions in a semi-enclosed sea. Ocean Engineering, 312, p.119131.
Oikonomou, C.L.G, Denaxa, D., and Korres, G., 2024: Formulating validation guidelines for marine renewable energy applications using the Copernicus Marine Mediterranean Sea waves reanalysis, 6th WCRP International Conference on Reanalysis, Tokyo, Japan, 28 Oct – 1 Nov 2024, OA1-02.
Oikonomou, C.L.G., Rizaev, I.G., Korres, G., Sheng, W. and Aggidis G., 2024. Exploring Uncertainties and Challenges in Wave Energy Resource Assessment, ISOPE International Ocean and Polar Engineering Conference, ISOPE-I-24-092
Zacharioudaki A., Ravdas M., Korres G. Wave climate extremes in the Mediterranean Sea obtained from a wave reanalysis for the period 1993 – 2020, J. Oper. Oceanogr., 15 (sup1) (2022), pp. s119-s126, 10.1080/1755876X.2022.2095169